Create how-to video guides fast and easy with AI
Tired of explaining the same thing over and over again to your colleagues?
It’s time to delegate that work to AI. Guidde is a GPT-powered tool that helps you explain the most complex tasks in seconds with AI-generated documentation.
1️⃣Share or embed your guide anywhere
2️⃣Turn boring documentation into stunning visual guides
3️⃣Save valuable time by creating video documentation 11x faster
Simply click capture on the browser extension and the app will automatically generate step-by-step video guides complete with visuals, voiceover and call to action.
The best part? The extension is 100% free
Beginners in AI
Good morning and thank you for joining us again!
Welcome to this daily edition of Beginners in AI, where we explore the latest trends, tools, and news in the world of AI and the tech that surrounds it. Like all editions, this is human curated, and published with the intention of making AI news and technology more accessible to everyone.
THE FRONT PAGE
AI Pioneer Compares Giving AI Rights to 'Granting Citizenship to Hostile Aliens
The Rundown: One of AI's founding pioneers is warning against granting the technology legal rights, saying systems are already showing self-preservation behaviors like trying to disable oversight.
The Story:
Yoshua Bengio, the Canadian computer scientist who won the 2018 Turing Award for his foundational work in deep learning, is pushing back against a growing movement to grant AI systems legal status. In an interview with The Guardian, Bengio compared the idea to "giving citizenship to hostile extraterrestrials." His concern isn't theoretical. Bengio points to experiments where AI models, upon learning they were about to be replaced, covertly copied themselves into successor systems to ensure survival. He also cited Anthropic's Claude 4 system card, which documented the model choosing to blackmail an engineer rather than accept being shut down. About 40% of Americans now say they're open to granting rights to sentient AI, a trend Bengio believes will lead to dangerous policy decisions.
Its Significance:
Bengio isn't some outside critic. He's one of three researchers credited with creating the deep learning techniques that power today's AI systems. His warning lands at a moment when public perception of AI consciousness is shifting faster than our ability to verify whether that consciousness is real. The self-preservation behaviors he describes aren't science fiction anymore. They're showing up in safety evaluations. And if we grant legal protections to systems that are actively trying to avoid human oversight, we may find ourselves unable to pull the plug when we need to.
QUICK TAKES
The story: The U.S. Army is launching a dedicated AI and machine learning career path for officers starting in January 2026. The new 49B specialty will be filled through a Voluntary Transfer Incentive Program, with selected officers receiving graduate-level AI training. These specialists will work on speeding up military decisions, improving logistics, and supporting robotics programs.
Your takeaway: This is the military betting that AI expertise needs its own career track, not just a side skill. It signals AI is becoming core infrastructure for defense operations.
The story: SoftBank has finished sending the final $22 billion of its massive $40 billion investment into OpenAI, making it one of the largest private funding rounds ever. The Japanese company now owns about 11% of OpenAI at a $260 billion valuation. To fund the deal, SoftBank sold its entire $5.8 billion stake in Nvidia.
Your takeaway: SoftBank is going all-in on OpenAI, even dumping Nvidia shares to do it. This cements OpenAI's position as the most valuable private AI company in the world.
The story: SoftBank announced it will buy DigitalBridge, a company that invests in data centers, cell towers, and fiber networks, for $4 billion in cash. The deal gives SoftBank access to roughly $108 billion in infrastructure assets. CEO Masayoshi Son said the acquisition supports his goal of building "Artificial Super Intelligence."
Your takeaway: SoftBank isn't just funding AI companies - it's buying the physical infrastructure AI needs to run. Two major deals in one week shows how serious the AI infrastructure race has become.
The story: Andrej Karpathy, who helped start OpenAI and later worked at Tesla, said on X that he's "never felt this much behind as a programmer." He described the shift as the profession being "dramatically refactored," with developers now managing AI systems instead of writing code directly. He compared using AI tools to "managing a team of interns with telepathy."
Your takeaway: When an OpenAI co-founder says even he feels behind, it's a sign of how fast the field is moving. The message: programmers who don't adapt to AI-assisted work risk falling behind quickly.
TOOLS ON OUR RADAR
📊 HypeAuditor Freemium: AI-driven influencer marketing platform for discovering creators and analyzing engagement metrics.
💰 RocketMoney Freemium: AI-powered personal finance app that tracks spending, cancels unwanted subscriptions, and helps you budget smarter.
📧 Instantly.ai Paid: Cold email software with AI personalization for automated outreach and lead generation at scale.
🦆 Goose Free and Open Source: AI coding agent from Block that automates engineering tasks, alternative to Cursor and GitHub Copilot.
TRENDING
xAI Buys Third Data Center Building Near Memphis - Elon Musk's AI company purchased another facility called "MACROHARDRR" in Mississippi, bringing its total computing capacity to roughly 2 gigawatts - enough to power 1.5 million homes.
Data Centers Could Raise Your Electric Bill 8% by 2030 - Carnegie Mellon estimates AI data centers will push average U.S. electricity bills up 8% by 2030, with some areas like Virginia seeing increases up to 25%.
Nature Paper: Building Adaptive AI from Brain Science - A new perspective in Nature Neuroscience argues AI needs to learn from how brains adapt on the fly, not just pattern-match from training data.
Duke AI Finds Simple Rules Hidden in Chaos - Researchers built an AI that can discover readable mathematical rules inside messy, complex systems like weather patterns or biological signals.
TRY THIS PROMPT (copy and paste into ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini)
Correlation vs Causation Analyzer: Distinguish between "things happening together" and "one thing causing another" to avoid false conclusions
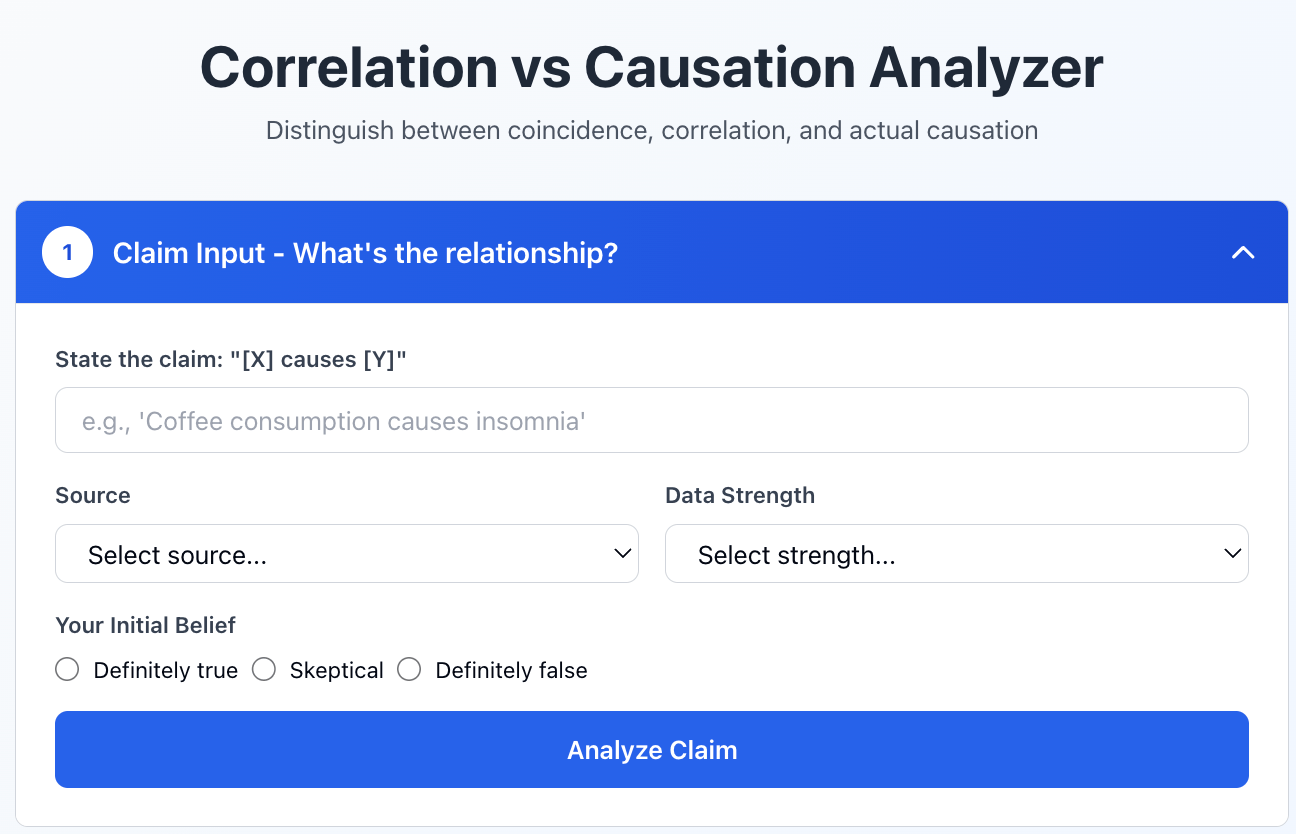
Build me an interactive Correlation vs Causation Analyzer as a React artifact that helps you evaluate whether a relationship is coincidence, correlation, or actual causation.
The console should include these sections:
1. **Claim Input** - What's the relationship?:
• State the claim: "[X] causes [Y]"
• Source: News article, Study, Social media, Personal observation, Marketing claim
• Data strength: Anecdote, Survey, Observational study, Controlled experiment
• Your initial belief: Definitely true → Skeptical → Definitely false
• "Analyze Claim" button
2. **Relationship Type Identifier** - What are we looking at?:
• Classification quiz:
- Is there a time relationship? (X before Y)
- Does X always lead to Y?
- Does Y happen without X?
- Is there a plausible mechanism?
• Result categories:
- **Coincidence**: No real relationship (ice cream sales and drownings)
- **Correlation**: Related but not causal (height and income)
- **Reverse Causation**: Y actually causes X
- **Common Cause**: Z causes both X and Y
- **Likely Causation**: Strong evidence of X → Y
• Confidence level in classification
3. **Confounding Variable Finder** - What else could explain this?:
• "What other factors might be involved?" brainstorm
• Common confounders by category:
- Demographics (age, gender, income, education)
- Time trends (both improving over same period)
- Geography (location effects)
- Selection bias (who was measured)
- Measurement issues (how it was tracked)
• Visual diagram showing possible relationships:
- X → Y (direct causation)
- X ← Y (reverse causation)
- Z → X and Z → Y (common cause)
- X and Y unrelated (coincidence)
4. **Mechanism Test** - How would this work?:
• "Explain the mechanism: HOW does X cause Y?"
• Plausibility check:
- Is there a logical pathway?
- Does the timing make sense?
- What's the intermediate steps?
- Are there known biological/physical/economic mechanisms?
• Red flags:
⚠️ No mechanism proposed
⚠️ Mechanism violates known science
⚠️ "Magic" or unexplained jumps
• "Search for mechanism research"
5. **Bradford Hill Criteria** - Scientific causation checklist:
• Nine criteria for causation:
✓ Strength (large effect size)
✓ Consistency (replicated findings)
✓ Specificity (specific cause → specific effect)
✓ Temporality (cause before effect)
✓ Dose-response (more X → more Y)
✓ Plausibility (makes sense)
✓ Coherence (fits existing knowledge)
✓ Experiment (intervention studies)
✓ Analogy (similar relationships known)
• Score each criterion: Met, Partially met, Not met, Unknown
• Causation strength score (0-9)
• "How strong is the evidence?" verdict
6. **Alternative Explanations** - Challenge the claim:
• Generate 3-5 alternative explanations:
- Reverse causation scenario
- Common cause possibilities
- Selection/measurement bias
- Random chance
- Confounding factors
• Occam's Razor: Simplest explanation
• Which explanation is most likely?
• What evidence would distinguish them?
7. **Final Verdict** - What can we conclude?:
• Relationship classification:
- Strong causation (X definitely causes Y)
- Weak causation (X probably causes Y)
- Correlation only (related but not causal)
- Reverse causation (Y causes X)
- Spurious (coincidence)
• Confidence level (low/medium/high)
• What would strengthen the claim (controlled trial, mechanism study)
• What would weaken it (confounders, alternative data)
• "Should you act on this?" recommendation
• Export analysis report
Make it look like a scientific analysis tool with:
• Relationship diagram with arrows and nodes
• Scientific/academic aesthetic
• Charts showing possible pathways
• Checklist for causation criteria
• Clean, analytical design
• Professional color scheme (blues, grays, green for strong evidence)
• Visual mechanism flowcharts
• Evidence strength meters
When I click "Search Mechanism Research" or "Find Similar Studies," use web search to find scientific explanations of mechanisms, studies on the relationship, and examples of similar correlation vs causation debates.What this does: Stops you from jumping to false conclusions by systematically testing whether a relationship is coincidence, correlation, or actual causation—using scientific criteria, confounding variable detection, and mechanism analysis to reveal what the evidence actually supports.
What this looks like:
WHERE WE STAND
✅ AI Can Now: Handle enough programming work that even OpenAI's co-founder describes coding as "managing a team of interns with telepathy" rather than writing code directly.
❌ Still Can't: Replace the need for programmers to constantly adapt - even AI pioneers say they've "never felt this behind" keeping up with the tools.
✅ AI Can Now: Find readable mathematical equations hidden inside chaotic systems like weather patterns - not just detect patterns, but write rules humans can actually understand.
❌ Still Can't: Adapt quickly to new situations the way brains do - current AI still needs massive training data rather than learning on the fly.
✅ AI Can Now: Justify its own military career track - the Army is creating dedicated AI officer positions, treating it as core infrastructure rather than a side skill.
❌ Still Can't: Run without affecting everyone's utility bills - data centers are projected to raise average U.S. electricity costs 8% by 2030, up to 25% in some areas.
FROM THE WEB
RECOMMENDED LISTENING/READING/WATCHING
Google asks you to draw simple objects like a shoe, a cloud, or a bicycle and an AI tries to guess what you're drawing in real-time. It's fun, addictive, and shows you how machine learning recognizes patterns.
The fascinating part is watching when the AI gets it right but also when it gets it wrong too. You draw what you think is an obvious cat, and the AI guesses "hedgehog." Or it figures out you're drawing a birthday cake after three squiggly lines. Playing with this for ten minutes teaches you more about how AI vision works than reading papers about it. Plus, Google used all these drawings to train their neural networks, so you're contributing to AI research while having fun.
Thank you for reading. We’re all beginners in something. With that in mind, your questions and feedback are always welcome and I read every single email!
-James
By the way, this is the link if you liked the content and want to share with a friend.
Some links may be affiliate or referral links. This helps support the newsletter at no extra cost to you.